Using REPL
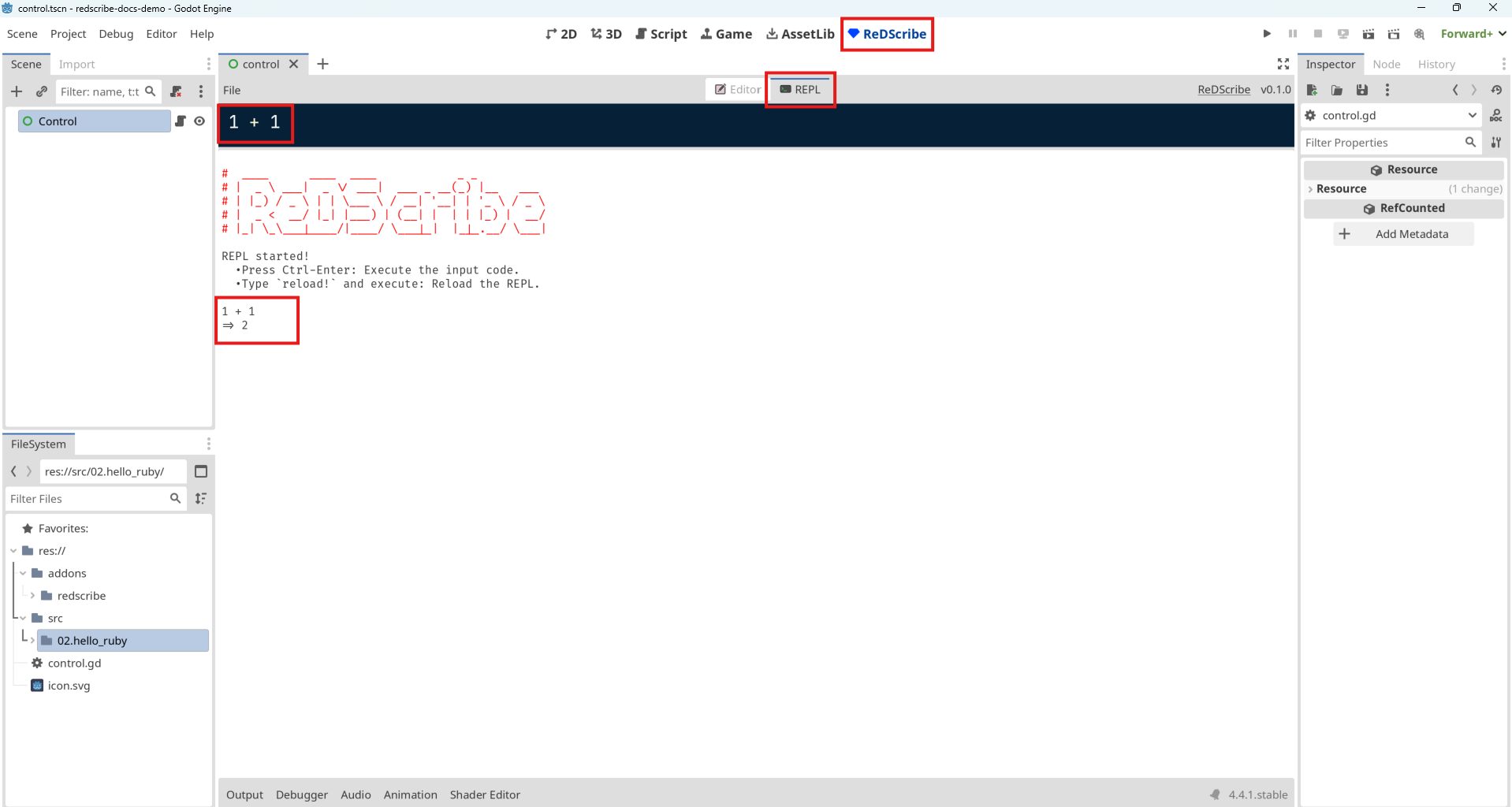
Open the REPL, type 1 + 1 and press Ctrl-Enter.
The result will be displayed.
The REPL supports several shortcuts.
Ctrl-uclears the input fieldCtrl-kdeletes text after the cursor in the input fieldCtrl-lclears the output fieldUp arrow (↑),Down arrow (↓)navigates through input field historyCtrl-[switches to the Editor tabCtrl-]switches back to the REPL tab
The REPL also supports multi-line input, with Enter as a newline.
Type the following and press Ctrl-Enter.
class Foo
def bar
'FooBar'
end
end
Foo.new.bar
=> "FooBar"
Emit signals
Try each of the following:
foo 'bar'
Godot.emit_signal :foo, 'bar'
[ foo ] method_missing: ["bar"]
=> <null>
[ foo ] signal emitted: "bar"
=> true
=> represents the return value of the method.
If any signal is emitted, it will be displayed in the output.

Red text is displayed when a method_missing channel signal is emitted, while blue text appears when a channel signal is emitted.
Define methods
Try the following:
@count = 0
def up
@count += 1
end
Then, try up a few times.
up
=> 1
up
=> 2
up
=> 3
100.times { up }
@count
100.times { up }
=> 100
@count
=> 104
Local variables are no longer available after execution.
So use instance variables like @count = 0 instead of count = 0.
Use require
mruby doesn't include require by default, but ReDScribe provides it as a helper method that loads Ruby files from the root of your Godot project.
require 'addons/redscribe/mrblib/math'
Run this, if the file loads successfully, it will return true.
The file is only loaded once—on subsequent calls, it will return false.
=> true
After executing require, try calling:
sin(1)
=> 0.8414709848079
addons/redscribe/mrblib/math.rb calls extend Math, making the sin method available.
extend Math
include Math
def π
PI
end
def √(x)
sqrt(x)
end
# ...
Reload and initialze the REPL
To initialize the REPL, run:
reload!
Once initalized, if you call the up or sin method again, you'll get method_missing.
up
sin(1)
[ up ] method_missing: []
[ sin ] method_missing: [1]
=> <null>
That's the basic usage of the REPL.
The REPL can be very helpful—feel free to use it whenever you like!